Ted Scott
January 24, 2024
If for some reason you are always putting things off “for later”, doing anything but important tasks, “congratulations”, most likely it means that you have procrastination. With this phenomenon sooner or later face all people on the planet. But when this way of life becomes a pattern, it negatively affects your work and career, and in your personal life. Then there is a need to get rid of the ailment.
What is procrastination in simple words

The term “procrastination” comes from Latin. It consists of two words: where “pro” means - “instead of” and “crastinus” - “tomorrow”, the definition in English will also not be different - “procrastination”. So procrastination is, in simple words, a persistent desire to put off important matters until tomorrow.
Sometimes procrastination is identified with laziness. But this is an erroneous opinion, because these two concepts differ in their essence. In fact, it is worth noting that the process is much more complex and profound than it may seem at first glance. A lazy person simply rests most of the time, and to procrastinate, it means to spend vital forces and energy on empty, unnecessary things. He understands the illogicality, incorrectness of his actions, which helps him to realize their negative consequences, experiencing a constant feeling of guilt.
A person turns on his computer to start work, the deadline for which is approaching by the hour, but remembers that yesterday he was going to call his sister. After a thirty-minute conversation, another pause follows: it’s time for a morning cup of coffee. Then someone calls again, and it’s “just around the corner” lunch time. As a result, he starts his main tasks at the very last moment, feverishly trying to meet the deadlines. He is nervous, berating himself, assuring himself that this is “the last time”.
On the one hand, self-avoidance of unpleasant situations or overly difficult tasks is a normal reaction of the psyche. In psychology, it is described as a defense mechanism that gets rid of the anxiety that arises when solving problems. But, when procrastination turns into a chronic form, its consequences will be quite unfortunate. In the long run, procrastinators face such problems as: severe forms of depression, job loss, lack of vitality.
Unlike laziness, which is caused by passive character, inertia and indecisiveness, procrastination arises from the refusal to take responsibility. If Alex is lying on the couch thinking: “I don’t feel like doing anything today. I’d better watch new YouTube videos” - this is a typical example of laziness. If his mind is spinning with thoughts like: “Man, I have so much to do today, and I’m lying on the couch” - this is already procrastination. A person does not refuse to fulfill obligations, but takes up work at the last moment. This is often due to the inability to properly assess its volume. The nature of such a phenomenon is not finally studied properly, so there is no consensus on the selection of means and methods to combat procrastination. The number of people in the world who face procrastination is constantly growing. In a few words, procrastination can be characterized as follows:
-
A person’s emotional reaction to unfinished business, manifested in a relaxed or tense manner.
-
Physiologically, the process arises from a conflict between two areas of the brain: the prefrontal cortex (the planning center) and the limbic system, which is responsible for pleasure.
Procrastination is not a disease, not a sign of weakness. Every person, regardless of temperament, mental abilities, is characterized by periodic postponement of things for later. It is necessary to deal with procrastination only when it affects vital processes.
Types of Procrastination

Procrastination as a psychological phenomenon has two forms of expression:
-
Passive. These are moments when a task is postponed because of decision-making problems.
-
Active. This is when procrastination becomes a kind of motivation, a challenge for active action.
American psychologist Stanley Milgram has identified the following types of procrastination:
-
Domestic, related to putting off regular household chores, such as doing the dishes or taking out the trash.
-
Neurotic, affecting vital decisions.
-
Academic, relating to all learning-related tasks.
-
Making decisions when, despite having all the necessary information and facts, they are put off “for tomorrow”.
-
Compulsive, evolving into a sustained behavioral pattern.
Procrastinators are divided into categories based on different behavioral patterns:
-
Perfectionists put off important tasks for fear of not meeting expectations. They fear that they will not do it perfectly.
-
Dreamers live in their own world, where everything is easy and simple, and are not ready to put their ideas into practice, the real stop makes them tense.
-
The restless are so afraid of change and loss of familiar comfort that they take no action to change anything about the way things are.
-
Crisis makers need an incentive to get to work. The threat of a deadline becomes the magic kick in the pants that forces them to pull themselves together.
-
The obsequious are willing to do anything to earn praise. They focus not on the quality of their work, but on the impression they make. As a result, they often never get to the real work, but make a lot of excuses to delay the fulfillment of their tasks.
-
Unruly are real rebels, not ready to “dance to someone else’s tune”. Promising to fulfill some task, they deliberately postpone the beginning of the process, thus demonstrating superiority and power over others. Yes, they will do it, but later.
For all its negative consequences, procrastination can be beneficial. Interestingly, according to American entrepreneur Paul Graham, there is a positive form of procrastination that does not require treatment or any adjustments. He categorized such procrastination into three types:
-
Absence of any action.
-
Replacing major tasks with other equally important things to do.
-
Getting more important, high priority things done.
Stanford University professor John Perry suggests that procrastination should be viewed as an organized phenomenon, structuring tasks so that the most important ones are at the top of the list and the unimportant ones at the bottom. This structure can be changed and unfolded as you like.
Causes of Procrastination

Various factors can be the catalyst for the development of procrastination. Work motivation is influenced by confidence in the success of work, the availability and size of remuneration, the adequacy of deadlines, and the desire to achieve goals. Among the main reasons that make you put things off for later, you can distinguish:
-
Lack of confidence in a positive result. When starting any business, a person assesses his chances of success. Because of low self-esteem, he postpones the beginning of active actions, because he is afraid that he will not do everything right.
-
Perfectionism, the desire to do everything perfectly. Realizing that he/she is not ready to perform the task at the moment 100%, a person stops himself, postponing it “until better times”.
-
Rebellion, disagreement with everyone in everything. Such procrastinators deliberately delay work, believing that they will do it better than others. But such procrastination leads to the exact opposite result, because the set tasks remain unfinished or are done hastily, at the last moment.
-
Lack of a sense of the value of work, causing the individual to tend to avoid it.
-
Physical or emotional fatigue that interferes with the realization of plans.
-
Various diseases associated with hormonal disorders, intoxication, neurological, mental problems.
Other common causes of procrastination:
-
Lack of a sense of time. Thinking that we have enough time at our disposal, we fall into a kind of trap. Experiencing a false sense of security, we unconsciously delay the deadline. But, the deadline comes unexpectedly and unnoticed.
-
Overestimating your capabilities. At the first glance at a task, it may seem that its fulfillment will take a little time. After all, you can write a simple article in a couple of hours or do a term paper in a few days, right? In fact, these processes take much longer. Without understanding all the peculiarities of the task, it is difficult to evaluate it objectively.
-
Waiting for “inspiration” or “working mood”. Some performers believe that any work should be approached in the right mood. But some tasks, especially difficult or unpleasant ones, it is better not to put off for later. After all, if you have to do them in a hurry, it will certainly not add motivation or pleasure.
Mental causes of procrastination
The tendency to procrastinate is not a disease. Under normal circumstances, it is a variant of the norm. But in some situations this phenomenon is considered a symptom of serious mental and psychological disorders, for example:
-
Depression accompanied by loss of energy, development of feelings of helplessness, insecurity.
-
Obsessive-compulsive disorder arising against the background of progressive perfectionism.
-
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, which causes a person to be distracted by internal thoughts or the environment, making it difficult for them to accomplish any task.
These diagnoses are made only by a physician, after a physical examination.
Consequences of deferring cases
Being prone to procrastination has many negative consequences:
-
Decreased self-esteem;
-
Increased anxiety, restlessness;
-
A life of constant stress;
-
Setbacks at work and at school;
-
Occupational burnout.
To avoid these problems, let’s understand how to deal with procrastination to eradicate it from your life for good.
How to fight procrastination: popular methods and techniques

First of all, what you need to do is to deal with the reasons for its occurrence. You should deal with unfulfilled tasks as you would with old things that have accumulated in your attic: sort through the shelves and throw away the excess. To a large extent, procrastination is not related to productivity, but to emotions. Therefore, you need to find a way to manage them competently, controlling your actions and behaviors.
Train yourself to see failures or mistakes as new opportunities for growth. Imagine the positive changes that will happen to you if you overcome them and solve the tasks successfully. Assess their relevance and usefulness. Make to-do lists, including tasks that you keep putting off. Set deadlines for them, add 20-30% of time to reserve so you don’t fall into a cognitive trap. Organize them into discrete milestones. Come up with a small reward for yourself for achieving each one.
Use popular time management techniques:
Eisenhower matrix
The method will help to properly organize and structure things both by priority and by due date. Divide all current tasks into groups:
-
Important and urgent;
-
Important but not urgent;
-
Not important, but urgent.
-
Not important and urgent.
First of all, start performing actions from the first category, then switch to the second, third group, and about the tasks that are in the 4th you can simply forget and without remorse to postpone “for later”.
Eliminating distractions
Everyone’s favorite chronophages: that social networks, that messengers, and also we should not forget about movies, talk shows or TV series, which constantly distract us from important things. For successful concentration on work it is convenient to use the Pomodoro method. Break down your work processes into 25-minute segments, scheduling 5-minute breaks between sessions.
Immediate fulfillment of unpleasant but important tasks
In time management, this technique is called “eat the frog”. Its authorship belongs to Brian Tracy, a Canadian motivational speaker and self-development specialist. You create a list of tasks, select the most difficult and important among them, immediately start it and do it to the end. After all, if you do urgent and serious things from the very morning, the rest of the day will pass more calmly.
Rewarding the achievement of intermediate goals
At the beginning of the road to success, it is difficult to imagine what the final result will be. But by noticing your small victories, it will be much easier to maintain enthusiasm and motivation. Noting your accomplishments at the end of the day will give you an extra push to keep moving forward.
Right motivation
One of the most effective tools to fight procrastination. Regularly remind yourself why you need to do it, why you are doing this or that task. Don’t use the phrase: “I have to”, replace it with “It’s my choice because”.
Formation of healthy habits
You may have to force yourself to do something first. Use your willpower, try to perform actions regularly. With good self-discipline, it will be easier for you to concentrate on doing important things.
Make yourself comfortable in your workplace. Put away unnecessary things, put your phone away. Delegate minor tasks to other people: relatives, colleagues, friends. They will perfectly cope with them without your personal presence. To avoid keeping a lot of unnecessary information in your head, use a convenient task manager, for example, LeaderTask planner.
Getting rid of procrastination with LeaderTask
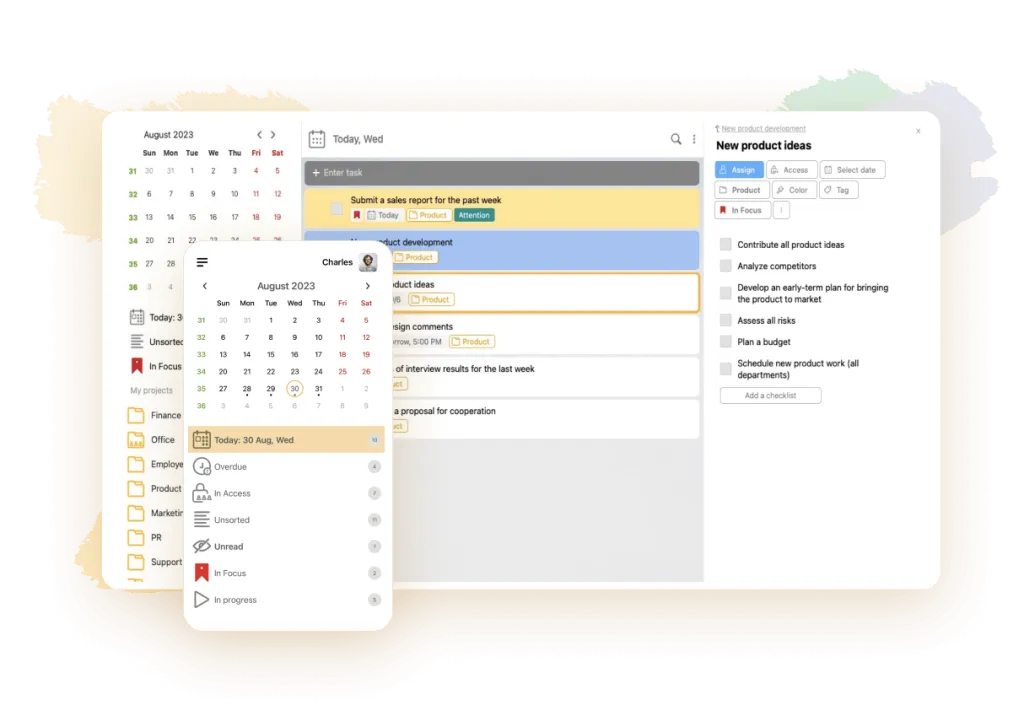
With this service, which combines an electronic diary, planner, CRM-system, project and task management software, you will make your life organized and understandable. In the application you can make to-do lists, set deadlines for them, adjust priority by highlighting important tasks with appropriate color marks, delegate tasks to subordinates, work in a team on common projects, see your productivity on the schedule and monitor the work of other employees.
You will learn how to stop putting things off, manage time, organize personal and work affairs using popular time management techniques. Don’t lose sight of any important details in your work, figure out how to achieve better results with less effort. The application works on all digital devices, including those without internet.
Conclusion
Procrastination is not a very useful condition, which worsens the quality of life and hinders career growth. But all people on Earth are subject to it to a greater or lesser extent. Do not worry too much if you periodically postpone important things for later. Do not try to make yourself a superhuman, never feeling tired or lazy. Forgive yourself for small weaknesses, reward yourself for small successes. Then you will be able to defeat procrastination and will face this phenomenon much less often.