December 26, 2023
Planning, systematic discussion of tasks is an important part of teamwork in any project. When there are two or three people in a team, it is easy to agree on controversial issues. But if the team grows to 10, 20 or more employees, opinions often diverge. Contractors working on the creation of a software product assess the labor intensity of the tasks assigned to them and their level of complexity in different ways. The concept of poker planning helps to come to a “common denominator”. This is a technology aimed at collective solution of any tasks in the process of creating a software product.
How the method works
Planning poker is a tool for assessing the complexity of work performed by a team. Its author is James Grenning, one of the authors of the Agile Manifesto, who first voiced this methodology in 2002. The method was further developed and popularized thanks to the work of co-author Mike Cohn, who described it in his work “Agile Estimating and Planning”.
Poker planning as a method of evaluation allows you to identify the main stages, well calculate the volume and complexity of tasks. All team members are involved in the evaluation: developers, testers, engineers, designers, analysts and other employees working on the project. The team evaluation used in this case gives an objective result. For example, a developer knows how much time his work takes, but may exaggerate its complexity in order to get more time to spare. Therefore, the results of the evaluation are always monitored by the manager acting as a facilitator. Until the end of the survey, none of the participants know the opinions of their colleagues. They are voiced at the same time.
The process of poker planning in Scrum resembles a game and its stages are as follows:
-
Each participant receives a set of cards with number points or alternative symbols. Usually the numbers from the Fibonacci sequence or various icons are used. For example, a “question” indicates that the participant is not sure of the answer, and a cup or a beer glass is a hint for a break in the discussion.
-
Regardless of the type of designation, the smallest number is assigned to the simplest cases. 0 is the simplest, which should not be included in the plan. 1-3 - simple tasks, 5-13 - medium complexity, 20-40 - large, 100 - global. Cases with the infinity sign are considered epochal in importance and magnitude.
-
The customer or product manager reads out the card. This is important to avoid a “broken phone” effect, where distorted information is passed from one participant to another.
-
The participants of the game are given time to think. Then they choose a card that corresponds to the complexity and importance of the task. They place this card on the table face up.
-
The cards are opened simultaneously. If there are serious differences of opinion, they are discussed with arguments in favor of one or another solution. If a participant rated a card as the simplest, he/she should explain how he/she plans to deal with its effective solution so quickly. The performers who gave the highest scores to the map also argue why they found it so difficult.
-
An additional round of evaluation is conducted. From the previously based data obtained during the game, a final decision is made.
Before starting with the cards, decide how the participants will play and how they will be evaluated. You need to decide whether you are going to assess the difficulty of the activity or the amount of time to complete it.
| Time | It is estimated how much time is needed for the solution. |
|---|---|
| Story Points | The complexity of backlog products is assessed. |
| Shirts | For evaluation purposes, the following conditional “sizes of shirts” are used: XS, S, M, L, and XL |
In a practical example, it looks like this:
-
So we have a task at hand. How long does it take to accomplish it?
-
The participants in the game silently reflect on what grade to give to the customer’s assignment.
-
The cards are revealed. Why are the opinions of participants A and B radically at odds with participant C? Let’s discuss what the problem is!
-
The cards are laid out again. An assessment is made, taking into account the previous discussion. With this, a common solution is reached.
Advantages of the technique
-
All team members are involved in the evaluation process.
-
The working group develops the same understanding by sharing experiences among the project participants.
-
Helps to find a perfect consensus in defining complexity.
-
Avoids the “anchoring effect”. If one or more participants say out loud a specific timeframe for completing a task (“I think it will take 6 days), other performers unconsciously anchor themselves to that number. That is, if someone has determined for himself or herself that it will take 3 days to complete the task, he or she will subconsciously increase his or her estimate.
What it is used for
Poker scheduling is productively used in software development in scrum teams working in agile methodology. The main goal of poker scheduling is not to set an exact deadline for a task, but to make sure that all team members understand the algorithm equally correctly. The method is suitable for teams that have enough time to reach consensus on controversial issues.
To make the technique more useful to the team, the following rules will help:
-
The discussion should be productive. Without stretching it out over time, a two-minute timer is set. When it goes off, the right to vote goes to the next team member. Then everyone will keep it brief.
-
It is better to divide the discussion into smaller sessions. Large groups can also be divided into smaller subgroups. Skype conferences with the use of electronic project management services can be organized when remote performers participate in the discussion.
-
Since most managers try to complete their work faster, their voting is often inefficient. But, they are more experienced compared to rank-and-file team members. If the difference in scores is small, choose the larger one. In some cases, managers are given veto power over team consensus.
-
Performers participating in the survey should have an idea of the complexity of the task based on past practical experience.
-
All assessments must be made synchronously! Otherwise, the participants will be oriented towards each other. This will minimize the objectivity of the planning. Set a timer on your phone or set a loud alarm clock.
-
Don’t ignore the break card. Some people need time to rest.
-
Hold meetings regularly, e.g. every two weeks or every other day, depending on the length of the sprints. This way you can keep all important tasks under control. If they take longer to complete, they will be discussed again.
LeaderTask app for project management
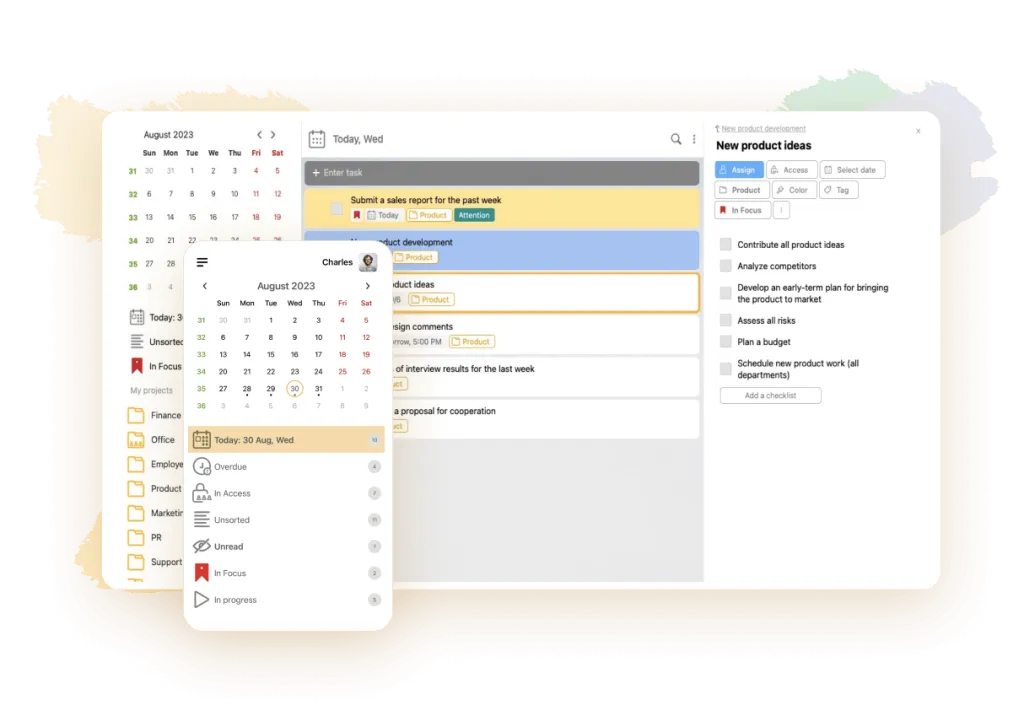
The Scrum planning methodology is suitable for effectively interacting teams. Various services and programs are used to organize communications between team members and provide remote online management of a team working according to the Scrum methodology. These include the LeaderTask application, which combines the functions of a Scrum manager, organizer, planner, and a modern project management system.
This online service replaces several popular planning applications, including Todoist or Trello. The functionality of the application includes data search, for easy retrieval of necessary information. It helps to efficiently distribute tasks between performers, plan their execution time, customize your work, track the final result and performance of each project participant. The application supports full functionality of agile methodologies, including electronic Kanban boards for visualization of tasks according to the Scrum system.
A convenient chat room is built into the program for discussing current issues on the project. It can be used for correspondence, voice messaging, agreement on attached documents. LeaderTask functions on all digital platforms, works without internet connection, in offline mode. It helps to speed up tasks and team projects.
Poker-based scheduling methodology is based on excitement, turning the routine process of setting deadlines for tasks into an exciting battle between team members. Helps set realistic deadlines. Fosters a shared understanding of the complexity of the project. During the estimation process, the team has fun and finds the best solution for the task, as close to realization as possible. This method is best suited for agile teams implementing the methodology in its entirety.