Max Miller
March 19, 2024
To successfully manage any team, it is important to correctly distribute roles and responsibilities among its members. To do this, you need to draw up a list of tasks, build a work plan, develop functionalities, divide the team into separate cells and interrelationships, try different methods of leadership, and make them interact effectively with each other. This is not difficult when there are 10-20 people in the subordination. But how to organise the work of a large company consisting of hundreds or thousands of employees? How do organise the management of these “cells” so that they work smoothly and rhythmically, like clockwork? This requires a system the organisational structure of management, which determines how to build links, hierarchy, distribution of areas of responsibility. We will try to deal with the topic of the organisational model of the enterprise in this article.
What is the organisational structure of a company, and why is it needed

Organisational structure of an organisation refers to a scheme or model that demonstrates the process of forming interactions between departments and management links of an enterprise. The organisational structure of a company is a package of official documents that reflect the hierarchy, quantitative composition, functions, responsibilities, rights of its elements. These include:
-
Documentation defining the main functions of structural units;
-
Regulations on the activities of structural units, describing in more detail the principle of building work in teams;
-
Job descriptions containing information on the roles and responsibilities of each performer;
-
A graphical diagram of an organisational structure representing the arrangement of a business.
Organisational structure of the organisation establishes the rights and responsibilities of managers. It serves as a basis for the development of job descriptions, descriptions of business processes. It helps to adjust the work of the enterprise, to establish links between all its departments. Organisational structure of the organisation binds the members of the collective into a single team, preserving the distinctive features and individuality of each member of the company’s organisational structure.
All enterprises form the organisational structure of the company for their own tasks, taking into account the business standards operating in the market. Modelling of the SWAp is necessary for all, regardless of the form of ownership and scale.
The organisational structure of the company allows the following objectives to be achieved:
-
Identify the areas of responsibility of each unit;
-
Allocate responsibilities among the performers;
-
Establish channels of communication and documentation transfer;
-
Find out the workload of staff to create a vacancy database.
It contains the following elements:
-
Management bodies (this is the manager or group of decision makers);
-
Enterprise rules (which may be documented, public or non-public, but are binding on all members of the workforce);
-
Division of labour (can be temporary or permanent, formal or informal).
The management structure is formed from a set of business goals and the tools available to achieve them. There are no firms that are completely similar to each other, they use their own approaches to management, focusing on mentality, customer needs, scale, and operations.
The following approaches are used to form organisational structures:
| Traditional | Management is distributed from top to bottom. There are no clear distinctions between management blocks. Suitable for small companies. |
|---|---|
| Organic | It is based on management flexibility and collegial decision-making. It is used when conducting business in unstable, frequently changing market conditions. |
| mechanistic | It is based on a rigid system of division of responsibilities. Executors are subordinate to the heads of blocks. As a result, the team works steadily and smoothly, like clockwork. |
Commercial enterprises are not obliged to streamline their activities. The development of a SWPPP is mandatory only for municipal or state-type institutions. But if this step is ignored, sooner or later an informal scheme of interaction between departments will still be formed. Otherwise, the business will simply cease to exist, as it will be impossible to manage. In order to avoid mistakes and critical miscalculations in building communications between divisions and departments, it is worth developing a management structure at the earliest stages of its existence.
How the organisational structure of a company is built
Before developing the company’s organisational structure, its owners, together with the manager, should identify possible business paths and appoint those responsible for the development of certain sectors. For this purpose:
-
A strategic plan is developed for a period of three or more years, which specifies the expected amount of investment, what services or products the company will produce, the scale of its development, and possible ways of promotion.
-
If there are several lines of business, they are segmented and a management and accountability system is developed.
-
After the analysis of strategic, current tasks, responsibility centres are defined and responsibilities are assigned to divisions, groups or departments.
According to Max Weber’s classical model, the organisational structure of an organisation is based on the following principles:
| 1. Allocation of responsibilities according to specialisation | Employees are assigned duties appropriate to their competences and qualifications. |
|---|---|
| 2. Hierarchical structure | Each manager must be in charge of the unit or department he is responsible for. Employees should have a clear understanding of what orders to follow. |
| 3. Allocation of responsibilities according to specialisation | All employees shall be governed by the general rules and standards approved for their positions. |
| 4. Impartiality, lack of personal interest in the performance of job duties | Personal sympathies should not influence decision-making processes. |
| 5. Opportunity for career growth and protection from arbitrary behaviour of superiors | A manager cannot dismiss an employee whose professional, personal qualities correspond to the position he holds without good reasons. An employee is promoted when his qualifications are improved. |
Among the main characteristics of new age organisational structures are such features as complexity, formalisation, centralisation. The complexity of the management scheme depends on the number of elements. This parameter is influenced by the degree of specialisation, the number of levels in the management structure, the peculiarity of location and interaction of its subdivisions.
To ensure efficient operations, the company’s organisational structure must be subordinate to production and change with it, reflect the scope of authority and functions of employees, as well as the specifics of the external environment in which the company operates.
Types of organisational structures

There are six types of basic organisational structures. They are used as a basis for building combined models that include some or other elements of OSP. Let’s consider the types of organisational structures, their features, pros and cons in more detail.
Linear
The simplest structure of an organisation is the linear traditional model, in which the organisation is top-down. The director of the company is subordinated to deputies responsible for certain blocks, under them are heads of departments and specialists.
Its advantages
-
Simplicity of organisational structure;
-
A clear division of functions and rights;
-
Formation of strict discipline with appropriate management style;
-
Quick installation of solutions;
-
Career development opportunities for performers who fulfil their duties with quality.
Disadvantages:
-
Lack of specialisation (one specialist can perform several functions at the same time);
-
Increased workload for management staff;
-
Authoritarianism;
-
Communication Difficulty.
This organisation structure is suitable for individual entrepreneurs and highly specialised companies (insurance agencies, cleaning services, etc.).
Functional
The functional organisational structure is built in the horizontal direction of management with clear specialisation of each area (block). This type also includes top management: general director, as well as top managers managing separate functional divisions, for example: director of marketing, finance, sales.
Advantages of this system:
-
Clear division of areas of responsibility;
-
No duplication of functions;
-
Quick Decision Making;
-
Equal contribution of each department and division to the common cause.
Minuses:
-
The likelihood of communication breakdowns;
-
Lack of overall technical leadership on projects and products;
-
Low personal accountability for the overall result;
-
Ineffective communication between employees from different departments.
This management model is more effective in combination with the linear management model. It is more suitable for holdings and teams with different activities.
Divisional
The divisional organizational structure of management implies division of the company into divisions, which are formed according to geographical location, products manufactured or end users. Each division has a manager who reports to the general management. One of the varieties of this model is the product or commodity management system, when the company is focused on the production of one or more products. The number of divisions and branches of the firm depends on their number.
Benefits:
-
Simplicity, efficiency;
-
Flexibility, adaptation to rapidly changing market conditions (non-performing structural units are easy to close);
-
Increased freedom for decision makers;
-
Excellent performance.
Weaknesses:
-
Competition among internal divisions;
-
Possibility of business slowdown due to increased number of organizational levels;
-
Difficulty in making strategic decisions due to the disconnection of divisions from each other.
-
Risk of uneven distribution of funds for the development of several structural elements.
Divisions work independently, are responsible for their own tasks, but are subordinate to the main management. Management solutions of this structure are suitable for companies with a large number of branches, producing several categories of products that require separate promotion on the market.
Matrix
Matrix management scheme is a combination of linear and program-target system. It is characterized by increased flexibility and complexity in subordination. In this way of working, the executors simultaneously report to the project manager and the heads of their departments. To fulfill the tasks of the project narrow specialists are obliged to perform additional functions. Employees are not released from their main duties and perform other tasks for a separate remuneration.
Pros:
-
Fast communication links between system elements;
-
Effective delineation of areas of responsibility;
-
High rates of development due to the independence of individual divisions;
-
Ease of developing and implementing a unified production policy;
-
Collaborative leadership style.
Disadvantages:
-
Increased communication and leadership requirements for functional elements;
-
Difficulty in decision making due to lengthy harmonization;
-
Risk of task incoherence as a result of simultaneous reporting to multiple managers;
-
Constant confrontation among structural units for funding, resources.
Project
The project management structure is used when creating a new business or innovative products, conducting large-scale developments, scientific and research studies. The elements of this structure are the general manager, project management, executives organized into groups.
Benefits:
-
Adaptability to market conditions, quick decision-making;
-
Hiring qualified, competent workers;
-
Resource Conservation.
Minuses:
-
High risks of error;
-
Lack of interest from the team to develop the project after delivery;
-
Dependence on the decisions of the project manager.
Formation of enterprise organizational structure with LeaderTask
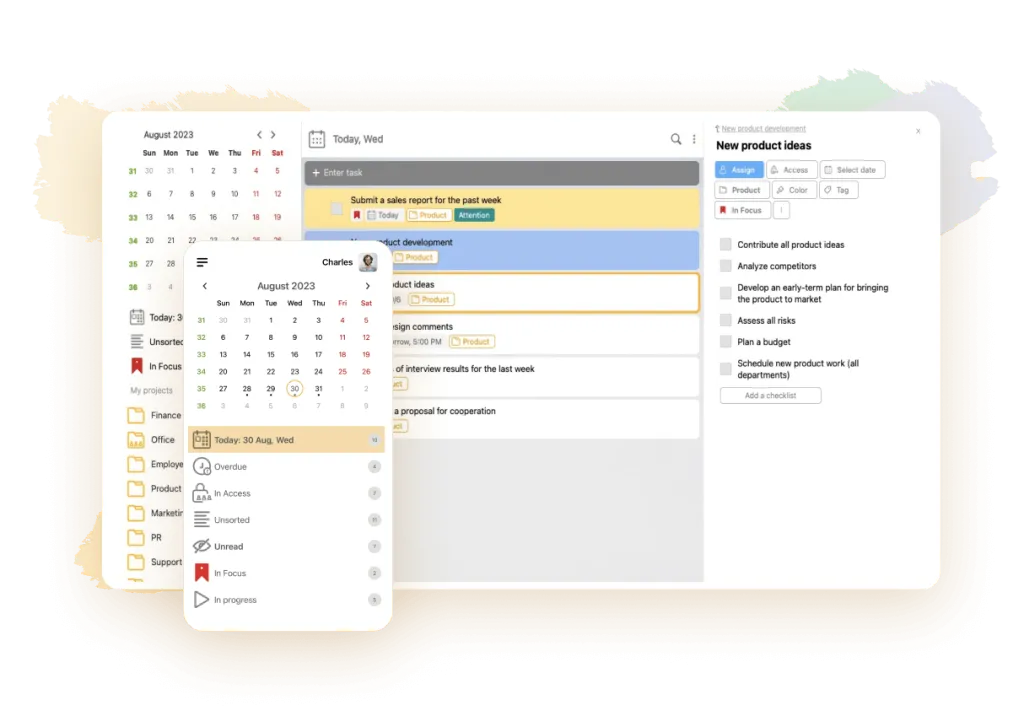
The development of an organizational structure is a complex process that requires a lot of time and certain knowledge on the part of the management. In order for the organization to work in an organized, coherent manner, like clockwork, it is necessary to develop job descriptions for all performers, distribute responsibilities, delineate authority between responsible persons. For this purpose, use a personal electronic assistant - LeaderTask application, an effective tool for managing any team.
The service is suitable for strategic, tactical and operational planning, employee communication, interaction in teams of any size and scale, including those involving remote employees. In the program it is convenient to create projects, goals and tasks, delegate to other executors, control the progress of execution. Add comments, notes, links and various files to tasks. Discuss work in the corporate chat, evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of staff. Manage at vertical and horizontal levels.
The app works across all digital platforms, including offline.
Conclusion
An effective management structure is necessary for the company’s development. It is worth avoiding excessive formalization and rigidity of management. The best results will be obtained by combining traditional and modern market models. When choosing a suitable system, you should also focus on the type of activity, the specifics of work and the scale of market presence.